Nematic phase: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Carl McBride (talk | contribs) m (Added an internal link) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:nematic_ellipsoid.png|Nematic phase for the hard 6x1x1 ellipsoid model. |thumb|right]] | [[Image:nematic_ellipsoid.png|Nematic phase for the hard 6x1x1 ellipsoid model. |thumb|right]] | ||
The nematic phase has orientational order, but no positional order | The '''nematic phase''' of a [[liquid crystals |liquid crystal]] has orientational order, but no positional order | ||
<ref>[http://www.oup.com/us/catalog/general/subject/Physics/MaterialsScience/?view=usa&ci=9780198517856 Pierre-Gilles De Gennes and J. Prost "Physics of Liquid Crystals" (1995)]</ref>. | |||
[ | |||
==Dielectric tensor== | ==Dielectric tensor== | ||
In the uniaxial nematic phase, defining the ''z''-axis to be parallel to the nematic axis, one has | In the uniaxial nematic phase, defining the ''z''-axis to be parallel to the nematic axis, one has | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
The response of a nematic liquid crystal | The response of a nematic liquid crystal | ||
to an external electric field depends on both the sign and the magnitude of <math>\Delta \epsilon</math>. | to an external electric field depends on both the sign and the magnitude of <math>\Delta \epsilon</math>. | ||
==Chiral nematic phase== | |||
See [[Chiral phases]]. | |||
==Discotic nematic phase== | |||
[[Image:discotic_nematic_ellipsoid.png|Discotic-nematic phase for the hard 6x6x1 ellipsoid model. |thumb|right]] | |||
==Biaxial nematic phase== | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.267801 Jorge Peláez and Mark R. Wilson "Atomistic Simulations of a Thermotropic Biaxial Liquid Crystal", Physical Review Letters '''97''' 267801 (2006)] | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2007.03.026 Carl McBride and Enrique Lomba "Hard biaxial ellipsoids revisited: Numerical results", Fluid Phase Equilibria '''255''' pp. 37-45 (2007)] | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2815804 Roberto Berardi, Luca Muccioli, and Claudio Zannoni "Field response and switching times in biaxial nematics", Journal of Chemical Physics '''128''' 024905 (2008)] | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/20/46/463101 Roberto Berardi, Luca Muccioli, Silvia Orlandi, Matteo Ricci and Claudio Zannoni "Computer simulations of biaxial nematics", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter '''20''' 463101 (2008)] | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3117925 Prabir K. Mukherjee and Kallol Sen "On a new topology in the phase diagram of biaxial nematic liquid crystals", Journal of Chemical Physics '''130''' 141101 (2009)] | |||
*[http://przyrbwn.icm.edu.pl/APP/ABSTR/120/a120-3-1.html A. Kapanowski "Statistical Theory of Biaxial Nematic and Cholesteric Phases", Acta Physica Polonica A '''120''' pp. 351-367 (2011)] | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3646310 Roberto Berardi, Juho S. Lintuvuori, Mark R. Wilson, and Claudio Zannoni "Phase diagram of the uniaxial and biaxial soft–core Gay–Berne model", Journal of Chemical Physics '''135''' 134119 (2011)] | |||
*[http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4771592 Akihiko Matsuyama "Novel biaxial nematic phases of side-chain liquid crystalline polymers", Journal of Chemical Physics '''137''' 224906 (2012)] | |||
* Geoffrey R. Luckhurst, Timothy J. Sluckin (Eds.) "Biaxial Nematic Liquid Crystals: Theory, Simulation and Experiment", Wiley-Blackwell (2011) ISBN 1444304550 | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | |||
[[category: liquid crystals]] | [[category: liquid crystals]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:15, 30 March 2016
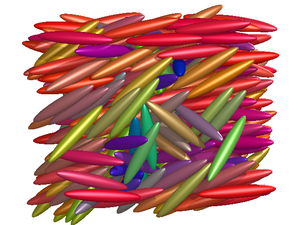
The nematic phase of a liquid crystal has orientational order, but no positional order [1].
Dielectric tensor[edit]
In the uniaxial nematic phase, defining the z-axis to be parallel to the nematic axis, one has
The anisotropy is defined as
- .
The response of a nematic liquid crystal to an external electric field depends on both the sign and the magnitude of .
Chiral nematic phase[edit]
See Chiral phases.
Discotic nematic phase[edit]
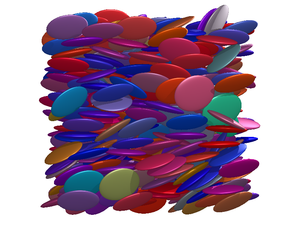
Biaxial nematic phase[edit]
- Jorge Peláez and Mark R. Wilson "Atomistic Simulations of a Thermotropic Biaxial Liquid Crystal", Physical Review Letters 97 267801 (2006)
- Carl McBride and Enrique Lomba "Hard biaxial ellipsoids revisited: Numerical results", Fluid Phase Equilibria 255 pp. 37-45 (2007)
- Roberto Berardi, Luca Muccioli, and Claudio Zannoni "Field response and switching times in biaxial nematics", Journal of Chemical Physics 128 024905 (2008)
- Roberto Berardi, Luca Muccioli, Silvia Orlandi, Matteo Ricci and Claudio Zannoni "Computer simulations of biaxial nematics", Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 20 463101 (2008)
- Prabir K. Mukherjee and Kallol Sen "On a new topology in the phase diagram of biaxial nematic liquid crystals", Journal of Chemical Physics 130 141101 (2009)
- A. Kapanowski "Statistical Theory of Biaxial Nematic and Cholesteric Phases", Acta Physica Polonica A 120 pp. 351-367 (2011)
- Roberto Berardi, Juho S. Lintuvuori, Mark R. Wilson, and Claudio Zannoni "Phase diagram of the uniaxial and biaxial soft–core Gay–Berne model", Journal of Chemical Physics 135 134119 (2011)
- Akihiko Matsuyama "Novel biaxial nematic phases of side-chain liquid crystalline polymers", Journal of Chemical Physics 137 224906 (2012)
- Geoffrey R. Luckhurst, Timothy J. Sluckin (Eds.) "Biaxial Nematic Liquid Crystals: Theory, Simulation and Experiment", Wiley-Blackwell (2011) ISBN 1444304550


